Belgian entrepreneurs face a unique challenge in today’s digital landscape: creating personalized experiences that resonate across three linguistic communities while maintaining GDPR compliance. After fifteen years of helping Belgian businesses navigate the complex world of website personalization, I’ve witnessed firsthand how proper A/B testing methodology can transform conversion rates and customer engagement.
The problem isn’t just about language barriers. It’s about understanding that a Brussels-based tech startup targeting both Flemish and Walloon markets needs fundamentally different approaches than a Ghent retailer focusing solely on Dutch-speaking customers. Belgian businesses often struggle with limited resources, fragmented markets, and the technical complexity of implementing effective personalization strategies.
In my experience consulting for companies across Belgium—from small family businesses in Antwerp to major corporations in Brussels—I’ve seen too many entrepreneurs abandon personalization efforts because they lack a structured methodology. This article provides that missing framework.

Understanding Belgian Market Dynamics
Belgium’s trilingual environment creates unprecedented opportunities for website personalization. Unlike our neighbors in France or the Netherlands, Belgian businesses must consider cultural nuances that extend beyond simple language translation. The purchasing behaviors of consumers in Flanders differ significantly from those in Wallonia, and German-speaking communities in the east have their own distinct preferences.
The Belgian e-commerce sales value was estimated at nine billion U.S. dollars in 2024, representing substantial growth potential for businesses implementing effective personalization strategies. However, this market isn’t uniformly distributed across regions, making targeted personalization essential for success.
Regional Personalization Considerations
When I worked with a Brussels fashion retailer last year, we discovered that Flemish customers responded better to minimalist design elements, while Walloon visitors preferred more elaborate product presentations. This insight came from systematic A/B testing across language segments, something that would be impossible without proper methodology.
The key lies in understanding that Belgian consumers expect localized experiences. They want to see prices in euros, shipping information relevant to their region, and customer service options in their preferred language. More importantly, they expect these elements to feel native to their cultural context, not merely translated.
Fundamental A/B Testing Principles
A/B testing methodology forms the backbone of effective website personalization. At its core, it’s about comparing two versions of a webpage to determine which performs better. But for Belgian entrepreneurs, this process must account for multilingual audiences and varying cultural expectations.
Statistical Significance in Small Markets
Belgium’s relatively small market size presents unique challenges for A/B testing. With fewer visitors per language segment, achieving statistical significance requires longer testing periods and more sophisticated methodologies. I typically recommend Belgian businesses plan for minimum sample sizes of 1,000 visitors per variation per language segment to ensure reliable results.
The mathematical foundation remains constant: you need sufficient data to confidently conclude that differences in performance aren’t due to random chance. For Belgian businesses, this often means running tests for 2-3 weeks longer than their international counterparts.
Sample Size Calculations
Calculating appropriate sample sizes for multilingual A/B tests requires careful consideration of your traffic distribution. If 60% of your visitors are Dutch-speaking, 35% French-speaking, and 5% German-speaking, you’ll need to adjust your testing strategy accordingly.
Here’s a practical approach I’ve developed for Belgian businesses:
Traffic Distribution Analysis: Monitor your analytics for at least 30 days to understand language-based visitor patterns. Consider seasonal variations, particularly for businesses serving tourist markets in Brussels or Bruges.
Segment-Specific Testing: Run separate tests for each language group when possible. A 20% improvement in conversion rates among Dutch speakers might require a different approach than achieving the same improvement among French speakers.
Cross-Cultural Validation: Test elements that work well in one language segment with other segments. Sometimes a successful Dutch personalization strategy translates well to French markets, but never assume this without testing.
GDPR Compliance Framework
European data protection regulations add another layer of complexity to website personalization in Belgium. The Data Protection Act does not contain additional rules to the GDPR for the use of personal data for the purposes of electronic marketing, meaning Belgian businesses must navigate both local and European requirements.
Consent Management
Effective personalization requires data collection, but GDPR mandates explicit consent for processing personal information. I’ve found that Belgian consumers are particularly privacy-conscious, often more so than the European average. This means your consent mechanisms must be crystal clear and culturally appropriate.
Language-Specific Consent: Provide consent forms in the user’s preferred language, not just a translated version. Legal terminology must be culturally appropriate and easily understood by local audiences.
Granular Permissions: Allow users to consent to specific types of personalization. Some visitors might accept product recommendations but reject behavioral tracking for advertising purposes.
Withdrawal Mechanisms: Make it easy for users to withdraw consent. Belgian consumers appreciate transparency and control over their data usage.
Technical Implementation Strategies
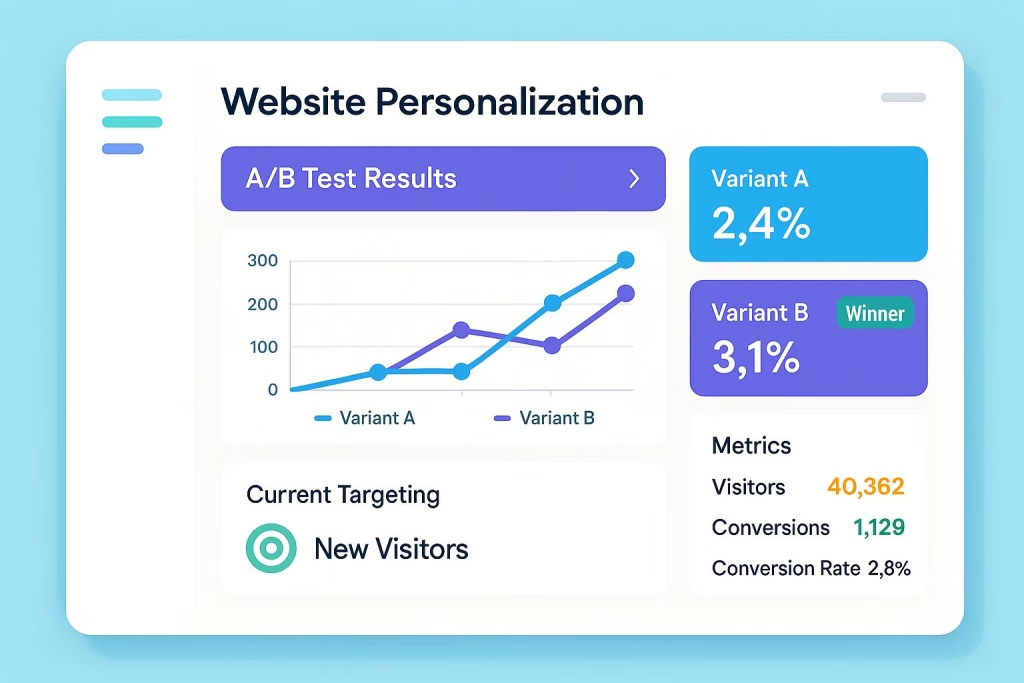
Testing Infrastructure
Building robust A/B testing infrastructure requires careful consideration of Belgium’s technical landscape. Many Belgian businesses operate on limited budgets, making tool selection crucial for long-term success.
Tool Selection Criteria: The number of tools in the optimization, personalization, and testing segment jumped from 230 to 271 in just one year, creating choice paralysis for many entrepreneurs. Focus on tools that offer multilingual support and GDPR compliance features.
Server-Side vs Client-Side Testing: Belgian businesses often benefit from server-side testing due to slower mobile connections in rural areas. This approach reduces page load times and improves user experience across all language segments.
Database Architecture
Storing personalization data for multilingual audiences requires thoughtful database design. I recommend separating user preferences by language while maintaining unified user profiles for cross-language insights.
Data Normalization: Structure your database to handle different cultural data formats. Belgian postal codes, for example, follow different patterns than international standards, affecting personalization algorithms.
Performance Optimization: Implement caching strategies that account for language-specific content delivery. Users in Liège shouldn’t wait for content cached in Antwerp servers.
Multilingual Testing Methodology
Language-Specific Variations
Testing across three languages simultaneously requires sophisticated experimental design. Simple translation isn’t sufficient—each language variant must account for cultural preferences and behavioral patterns.
Content Adaptation: Beyond translation, consider cultural adaptation. Color preferences, imagery choices, and even layout preferences vary between linguistic communities. What works in Flemish markets might fail in Walloon regions.
Seasonal Considerations: Belgian regions celebrate different holidays and have varying shopping seasons. Personalization strategies must account for these temporal variations across language segments.
Cross-Language Insights
One of the most valuable outcomes of multilingual A/B testing is discovering insights that transcend language barriers. Sometimes a successful German-language personalization strategy reveals universal principles applicable across all Belgian markets.
Universal Patterns: Look for personalization elements that consistently improve performance across all language segments. These often become cornerstone strategies for broader implementation.
Cultural Bridges: Identify common ground between linguistic communities. Brussels’ multilingual population often serves as a testing ground for cross-cultural personalization strategies.
Advanced Personalization Techniques
Behavioral Segmentation
Personalized experiences generate 41% more impact than general ones, making behavioral segmentation crucial for Belgian businesses. However, cultural context must inform these behavioral patterns.
Purchase Timing: Flemish consumers often research extensively before purchasing, while Walloon customers might make quicker decisions. Personalization strategies must account for these different decision-making processes.
Device Preferences: Mobile usage patterns vary significantly across Belgian regions. Urban Brussels users might prefer mobile-first experiences, while rural Flemish customers still favor desktop interactions.
Dynamic Content Strategies
Implementing dynamic content requires balancing personalization with performance. Belgian businesses must consider slower internet speeds in rural areas while delivering rich, personalized experiences in urban centers.
Content Prioritization: Display the most relevant content first, especially for mobile users. This might mean showing local store information prominently for Antwerp visitors while featuring shipping options for Brussels customers.
Progressive Enhancement: Build your personalization layer on top of a solid, universally accessible foundation. This ensures all users receive value regardless of their device or connection speed.
Measuring Success Metrics
Key Performance Indicators
Defining success metrics for multilingual personalization requires careful consideration of cultural differences in user behavior. What constitutes a successful conversion varies between Belgian regions and languages.
Conversion Rates: Track conversion rates separately for each language segment. A 5% improvement in Dutch-language conversions might require different optimization than achieving similar results in French markets.
Engagement Metrics: Time on site, page views, and bounce rates provide insights into cultural preferences. Flemish users might prefer detailed product information, while Walloon visitors respond better to visual presentations.
Customer Lifetime Value: Measure long-term value creation across language segments. Sometimes lower initial conversion rates in one language segment yield higher lifetime value.
Attribution Modeling
Belgian businesses often struggle with attribution in multilingual environments. Customers might research in Dutch but purchase in French, making traditional attribution models inadequate.
Cross-Language Attribution: Implement tracking that follows users across language preferences. This provides more accurate insights into personalization effectiveness.
Cultural Attribution: Consider cultural factors in attribution modeling. Business customers in Brussels might follow different purchase paths than individual consumers in Ghent.
Common Implementation Challenges
Resource Constraints
67% of companies reported resources for personalization are limited or not available due to lack of time or budget, a challenge particularly acute for Belgian SMEs. Smart resource allocation becomes essential for success.
Phased Implementation: Start with high-impact, low-effort personalizations. Language-based welcome messages often provide significant returns with minimal investment.
Automated Systems: Implement automation wherever possible to reduce ongoing maintenance costs. This is especially important for businesses managing three language variants.
Technical Complexity
Managing multilingual personalization creates technical challenges that many Belgian businesses underestimate. From character encoding to database optimization, the technical requirements multiply with each language addition.
Infrastructure Planning: Design your technical infrastructure to handle multilingual complexity from the start. Retrofitting single-language systems for multilingual use often costs more than building correctly initially.
Maintenance Considerations: Plan for ongoing maintenance across all language segments. Security updates, content management, and performance optimization must consider multilingual requirements.
Future Trends and Opportunities
AI-Driven Personalization
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing personalization capabilities, offering Belgian businesses unprecedented opportunities to serve their multilingual markets more effectively.
Machine Learning: AI systems can identify patterns across language segments that human analysts might miss. This capability is particularly valuable for Belgian businesses serving diverse linguistic communities.
Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics can predict user preferences based on cultural and linguistic patterns, enabling proactive personalization strategies.
Voice and Visual Search
Emerging technologies like voice search present unique opportunities for Belgian businesses. Voice search patterns differ significantly between Dutch, French, and German speakers, requiring specialized personalization approaches.
Multilingual Voice: Implement voice search capabilities that recognize and respond appropriately to Belgium’s three official languages.
Visual Recognition: Visual search technologies can bridge language barriers, allowing customers to find products regardless of their linguistic preferences.
Actionable Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-2)
Start with basic multilingual infrastructure and GDPR compliance. Implement proper analytics tracking and consent management systems before beginning personalization efforts.
Technical Setup: Configure analytics to track language-specific user behavior. Implement proper consent management that complies with Belgian and European regulations.
Content Audit: Review existing content for cultural appropriateness across all language segments. Identify quick wins for basic personalization implementation.
Phase 2: Basic Personalization (Months 3-4)
Implement fundamental personalization features like language-based welcome messages and region-specific content display.
Language Detection: Implement automatic language detection while allowing user override. Respect user preferences while providing appropriate defaults.
Regional Customization: Display region-specific information like local store locations, shipping options, and customer service contacts.
Phase 3: Advanced Testing (Months 5-6)
Begin systematic A/B testing across language segments. Focus on high-impact elements like checkout processes and product recommendations.
Systematic Testing: Implement regular testing schedules for each language segment. Document results and insights for future reference.
Cross-Language Analysis: Analyze results across language segments to identify universal improvement opportunities.
Phase 4: Optimization and Scale (Months 7+)
Refine personalization strategies based on test results. Implement advanced features like predictive personalization and dynamic content optimization.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor personalization performance across all language segments. Adjust strategies based on changing user behavior and market conditions.
Expansion Planning: Plan for scaling personalization efforts as your business grows. Consider new technologies and emerging opportunities in the Belgian market.
Website personalization through systematic A/B testing methodology offers Belgian entrepreneurs a powerful tool for competing in today’s digital marketplace. The key lies in understanding that successful personalization requires more than translation—it demands cultural sensitivity, technical excellence, and commitment to ongoing optimization.
By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, Belgian businesses can create personalized experiences that resonate with their multilingual audiences while maintaining GDPR compliance and technical performance. The investment in proper methodology pays dividends through improved conversion rates, enhanced customer satisfaction, and sustainable competitive advantage in Belgium’s unique market environment.
Remember that personalization is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Start with solid foundations, test systematically, and always prioritize user experience over technical complexity. Your Belgian customers—regardless of their language preference—will appreciate the effort you invest in creating personalized experiences that truly understand and serve their needs.